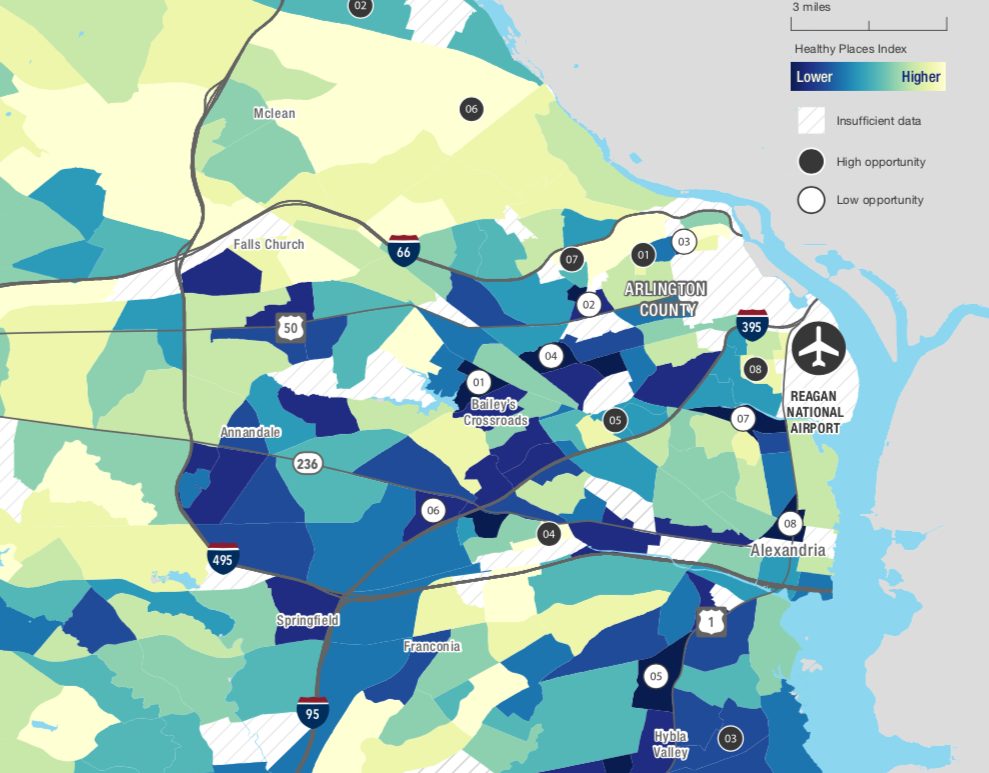
New research suggests that people living in Arlington’s poorest neighborhoods also have the fewest opportunities to lead healthy lives when compared to other communities throughout the entire D.C. region.
A study commissioned by the Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments and conducted by researchers at Virginia Commonwealth University show that many of Arlington’s most diverse neighborhoods with the lowest median incomes, such Columbia Heights, Nauck, Douglas Park and Buckingham, also scored the lowest in their measure of “health opportunities” across metropolitan Washington. The results closely mirror a previous study’s findings that people living in many of the same neighborhoods lack economic opportunities as well.
The researchers developed a “Healthy Places Index,” known as HPI, to evaluate not only health outcomes (like life expectancy) in each community, but also to understand whether people have the opportunity to be healthy based on where they live. That includes evaluations of factors like air quality, access to healthcare, housing affordability, the availability of public transportation and education levels.
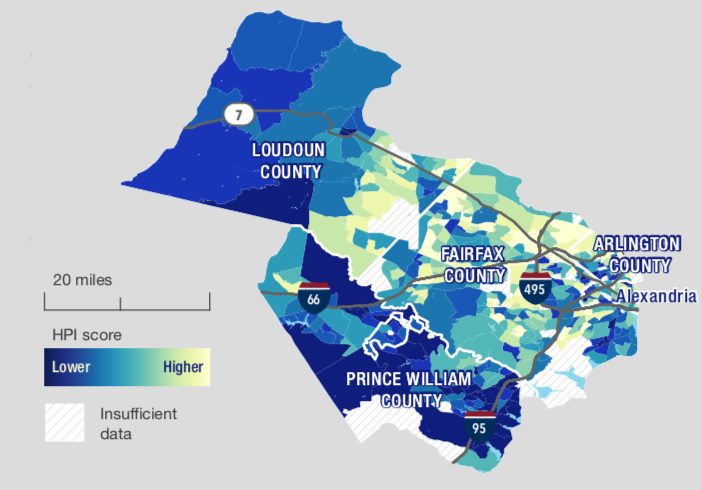
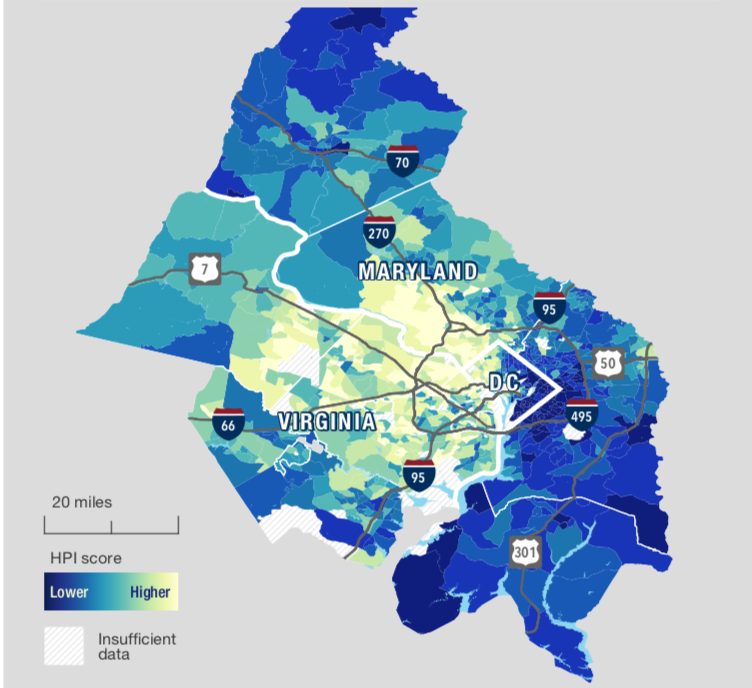
The study applies that index to neighborhoods across the D.C. area, examining communities using granular Census tract designations to detect patterns within counties and cities in the region. Though the group found that the overall health of the 4.5 million people living in the District and its suburbs is “excellent” and “well above the national average,” they also uncovered “islands of disadvantage” within even wealthy localities like Arlington.
Even though some of the more affluent, higher educated areas of the county rate quite highly in the study’s measure of health opportunities, others rank among the lowest in all of Northern Virginia. The researchers identified the Columbia Heights neighborhood, just off Columbia Pike, as having one of the “the lowest HPI scores in the region,” noting that about 23 percent of adult residents there live in poverty. Buckingham, located along Route 50, also posted poor HPI scores, and the study noted that its residents have a median income of about $38,125 annually.
“The researchers found stark contrasts in socioeconomic and environmental conditions in Northern Virginia, often between neighborhoods separated by only a few miles or blocks,” the VCU academics wrote. “As was observed elsewhere in the region, people of color were disproportionately exposed to adverse living conditions.”
To illustrate those points, the study compared McLean — one of the wealthiest and whitest communities in the area — to Columbia Heights. The former ranked among the top-scoring neighborhoods in the region on the HPI, a far cry from Columbia Heights’ own performance.
“The population in the McLean tract was predominately white (70 percent) and Asian (19 percent), the population in Columbia Heights was largely Hispanic (51 percent) and black (19 percent),” the researchers wrote. “More than half was foreign-born, and most immigrated during 2000-2009.”
While the researchers identify a whole host of factors that could be contributing to such a split, they also stress that it is impossible to ignore the impact of “institutional racism” in understanding why such a divide exists between the races when it comes to health opportunities. They note that discriminatory housing and economic policies mean that people of color are “more likely to live in racially and ethnically segregated neighborhoods that suffer from decades of disinvestment,” which can have a whole host of negative consequences for their health.
“As a result, neighborhoods of color often lack access to affordable high-quality housing, stores that sell healthy foods, green space, clean air and clean water,” the researchers wrote. “These communities are often targets for fast food outlets, tobacco and alcohol marketing and liquor stores. These conditions affect not only the health, economic opportunity, and social mobility of people of color, but they also weaken the health and economy of the entire region.”
Accordingly, the study recommends approaches recognizing that history to officials sitting on the Council of Governments, as they try to craft a response across the region.
“Real solutions require targeted investments in marginalized neighborhoods to improve access to affordable, healthy housing as well as affordable transportation, child care, and health care (e.g., primary care, dental care, behavioral health services),” they wrote. “Everyone benefits from this approach, not only the residents in low-income neighborhoods and communities of color, but also the entire regional economy. Economic and racial inequity saps the strength of the economy. Everyone pays a price for inaction: persistent poverty and social isolation fuel discontent, unhealthy behaviors (e.g., drug addiction), crime, and violence.”