A new report says some levels of pollution are down in the Potomac River, but cautioned that the once-troubled waterway isn’t out the woods yet.
Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments analyzed data collected between 1985 and 2016 and found that “water quality improvements have reduced pollution significantly.”
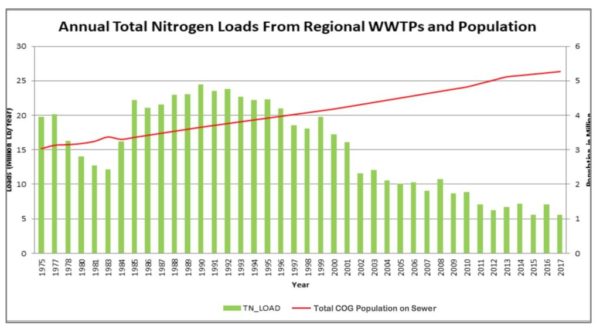
MWCOG’s 27-page report said two substances in particular have noticeably decreased: nitrogen and phosphorus.
Both are common nutrients for soil and water, but runoff from farms and waste treatment facilities can lead to excess amounts flowing into waterways. When too much nitrogen enters a river it can cause plants to overgrow and choke the oxygen from the water, killing fish and in some cases making the water toxic to young children.
Too much phosphorus causes algae blooms that are deadly to fish. Blooms have been spotted north of Chain Bridge, according to the report.
MWCOG’s report released on Wednesday said its pollution analysis found that:
The amounts of nitrogen and phosphorus — which, in excess, contribute to water quality problems — contained in the discharge from wastewater plants in metropolitan Washington has declined dramatically since the 1980s and is on track for further reductions. The number and extent of harmful algal blooms in the upper Potomac estuary has declined significantly. Populations of aquatic plants and animals that live in this portion of the river, such as submerged aquatic vegetation, some fish, and some waterfowl have grown closer to their historical abundances.
“Scientists are still interpreting how much time elapses between various nutrient reduction efforts and when their impact shows up in the Potomac estuary and the [Chesapeake] Bay,” the report notes. “What is certain is that additional efforts to reduce nutrients and sediment from agriculture and urban runoff will be needed to achieve the river’s long-term water quality goals.”
The report says local governments are working to reduce other contaminants like mercury, prescription drugs, and chemicals like polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs).
Last year, Potomac Conservancy, an advocacy nonprofit, gave the river a “B” rating. That’s a big improvement from the “D” rating the group gave it 10 years ago.
Potomac Conservancy noted that with less pollution people are increasingly using the river “as a place to hangout, recreate and live.”
In the future, citizen scientists are likely to be a part of making these reports happen. Last month, people volunteered to start collecting weekly water samples of the Potomac and the Anacostia so scientists can track E. coli levels in both rivers.
Local governments have spent billions over the last three decades to clean up the rivers, mainly by redirecting sewage flows, and managing stormwater runoff better.
In Arlington, volunteers have cleaned up trash along streams and riverbanks for three decades.
Image (top) via Flickr pool user Wolfkann, chart (middle) via MWCOG