
An estimated 7.8% of Arlington households experienced food insecurity in 2019, according to a new report.
The report, completed by Urban Institute in partnership with Arlington County Food Security Task Force, provides a snapshot of the financial and food challenges for Arlington households, including in otherwise pricey parts of town like Crystal City and Pentagon City.
“Despite the area’s reputation as wealthy and well-resourced, more than 6,700 of the county’s 108,604 households were referred to the Arlington Food Assistance Center in 2021, signaling that this abundance is not shared by all residents,” the report says.
The report made many recommendations to the county, including to incentivize affordable grocers, offer gas cards, subsidize public transportation, expand SNAP outreach, provide grocery gift cards, subsidize or waive grocery delivery fees for SNAP participants, and open more free food distribution sites in higher need areas.
The study, conducted last year and released this month, indicated food insecurity rates were higher particularly in the Glencarlyn, Buckingham, Ashton Heights, Pentagon City, Crystal City, Forest Glen, Arlington Mill neighborhoods.
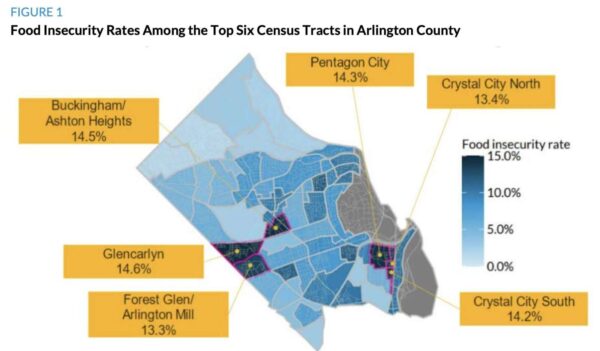
“We surveyed residents living in four neighborhoods with the highest food insecurity rates (from 13.3 to 14.6 percent) in the county and found that residents were more likely to rent their homes and have low incomes, and 17 percent were Social Security beneficiaries, which suggests they are living on a fixed income,” the report says.
For residents experiencing food insecurity, budgets for food were often the first to be cut in order to pay bills like rent and utilities. Some of the factors affecting the ability to buy food included the local food environment, labor market, transportation, housing, child care and debt.
Food accessibility
The study considered grocery store or other non-convenience retail food locations accessible if they were within 40 minutes of roundtrip travel. Such stores were accessible to most residents, even those that lived in neighborhoods with high estimated food insecurity rates.
But residents that were surveyed prioritized groceries’ cost when determining where to shop, making it more challenging to afford healthy food.
“Residents reported some challenges in paying for groceries, especially meat, as the cost of food increased 6.3 percent (and 14.8 percent for meat) between December 2020 and December 2021,” the report said.
Those who were food insecure were more likely to walk, get a ride or use Metro to get groceries than those who were food secure and likely own a car. About half of the residents experiencing food insecurity during the survey used free groceries or meals, according to the report, and most of those residents said they accessed those resources one to three times each month.
While the Crystal City and Pentagon City areas had relatively high estimated food insecurity rates compared with the rest of the county, they had low access to existing charitable food resources.
Food insecurity disproportionately affects Black, Hispanic, and Asian households in Arlington, according to the report. Asian households with low incomes, of which there was a concentration in the Crystal City area, had to travel farther to access charitable food sites, compared with Black and Hispanic households.
Arlington County says it’s reviewing the report.
“The Food Security Task Force is reviewing findings and recommendations from the study, and will consider investments where Arlington County could build on its strengths and address residents’ concerns and barriers,” a newsletter from Arlington Department of Human Services said.

